Leaf Spring Support Hinge Design
The master leaf of a laminated leaf spring is hinged at the supports. The support forces induce, stresses due to longitudinal forces and stresses arising due to possible twist. Hence, the master leaf is more stressed compared to other the graduated leaves. Methods to reduce additional stresses could be,
1. Master leaf is made of stronger material than the other leaves.
2. Master leaf is made thinner than the other leaves. This will reduce the bending stress as evident from stress equation.
3. Another common practice is to increase the radius of curvature of the master leaf than the next leaf.
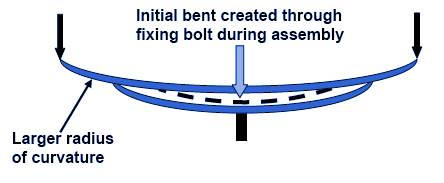
The master leaf has a larger radius of curvature compared to the additional leaf that is placed below so obviously a gap will be created between the two leaves as indicated in the figure. Now, an initial bent is created during assembly by tightening the central bolt. Therefore, some amount of compressive stress will be produced at the inside curvature of the master leaf. Similarly, at the outside curvature of the master leaf tensile stress will be produced.
Both these stresses are initial stresses in the master leaf. However, by such operation of tightening the central bolt, the additional leaf that is placed beneath the master leaf has a tendency to flatten out and as a result the stress pattern of the additional leaf will be reverse of that of the master leaf, tensile stress is produced at the inner curvature and compressive stress is produced at the outer curvature. Hence, when the spring is loaded, for both the master leaf and the additional leaf, tensile stress will be produced at the inner curvature and compressive stress will be produced at the outer curvature.
Therefore, due to opposite nature of initial stress and loading stress, the master leaf will experience lesser stress on both the surfaces. However, due to same nature of initial stress and loading stress, the additional leaf is stressed more compared to the master leaf. But, it is to be noted that the higher stress on the additional leaf is actually shared between all other leaves than the master leaf. This practice of stress relief in the master leaf is known as Nipping of leaf spring. As a matter of fact, all the leaves of a laminated leaf spring do have certain amount of nipping, so that there will be gaps between the leaves, as a result the stresses will be uniformly distributed and accumulated dusts can also be cleaned.
Sample Calculations:
Design a leaf spring to carry a load of 3400N and placed over a span of 800 mm. The spring can deflect by 50mm. Consider, allowable bending stress for the spring material as 350 MPa and E=2 (10)5 MPa.
Let us consider the design to be based on uniform strength beam.
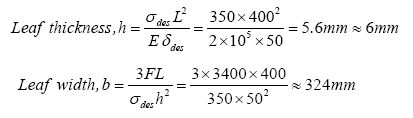
It is observed that the width is too large to accommodate as a machine member. Hence, if we consider, say 6 springs, then width of each spring becomes 54mm.