Related Resources: fluid flow
Pitot Tube Theory and Application
Pitot Tube Theory and Application
This instrument is very important in aviation to calculate the speed of airplanes with respect to the air.
The animation below shows an airplane Pitot tube and the relationship between its speed and the height of the second tube.
This relationship is explained by the Bernoulli equation:
The equation in this case means that at two different points (1 and 2) of a runoff, the total energy remains constant,
This energy consists of the potential energy due to head (z), flow velocity (v) and pressure (P).
Points (1) and (2) are taken according to the following figure:
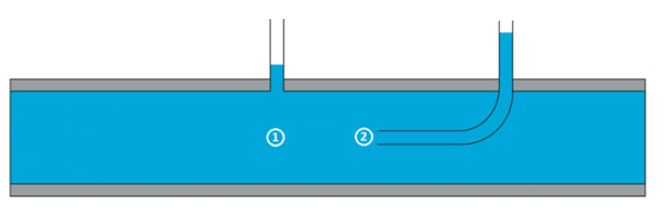
At point (1) and (2) the head z is the same, while at point (2) the flow velocity is 0, so the equation reduces to:
To obtain the pressures in (1) and (2), the height of the fluid in the respective tubes is measured, according to the figure:
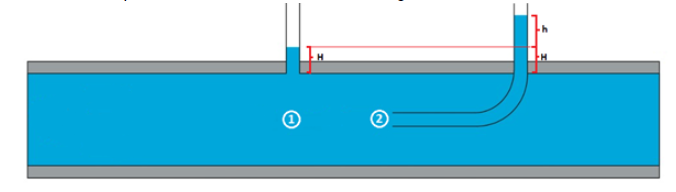
The hydrostatic pressure is calculated at both points:
Hydrostatic pressure:
On point (1):
At point 2:
With which the equation remains:
It is in this expression where we can see that the increase in measurement height is due to the kinetic energy at point 2 of the fluid.
This energy is transformed into pressure as it travels through the tube and causes the fluid to rise in h. Finally, we clear ν 1 :
As you can see, the calculation of the velocity does not depend on the density of the fluid or its specific weight, only the height h of the tube (2).
Related:
- Pitot-Static Tube Air Velocity Calculator and Equation
- Stagnation Pressure Incompressible Fluid
- Instrumentation, Electronics & Control Sensing Devices
- Pitot Tube Type Flow Detector Pitot tube is a pressure measurement instrument used to measure fluid flow velocity.
- Gas Flow Rate Through Orifice Equations and Calculator per. ISO 5167 ISO 5167 is applicable to orifice plates, nozzles and Venturi tubes when they are inserted in a conduit running full to determine the flow rate of the fluid flowing in the conduit.
- Gas Compressibility Factor (Gas Deviation Factor)
- Gas Flow Under Laminar Viscous Conditions Equations and Calculator
- Gas Material Balance Equation
- General Energy Equation Conservation of energy principle states that energy can be neither created nor destroyed.
- Simplified Bernoulli Equation Steady flow system in which no work is done on or by the fluid, no heat is transferred to or from the fluid, and no change occurs in the internal energy
- Head The term head is used by engineers in reference to pressure.
- Energy Conversions in Fluid Systems Energy Conversions in Fluid Systems Bernoulli's Equation
- Restrictions on the Simplified Bernoulli Equation Restrictions on the Simplified Bernoulli Fluid
- Extended Bernoulli Bernoulli equation can be modified to take into account gains and losses of head.
- Application of Bernoulli's Equation to a Venturi A venturi, may be analyzed using Bernoulli's equation and the continuity equation.
- Siphon Flow and Discharge Rates Tables and Charts
- Siphon Flow Rate from Small Pipes Equation and Calculator
- Siphon Discharge Rate Equations and Calculator
- Babcock Steam Flow Rate Formula and Calculator An empirical equation for steam flow is the Babcock formula.
- Unwin Gas Change of Pressure and Calculator and Formulas The Unwin formula has been successfully used in steam piping calculations for many years.
- Water Vapor Density atmosphere Equation - Water vapor in the atmosphere obeys the ideal gas law,
- Vapor Pressure Spreadsheet Calculator
- Viscosity of a Pure Liquid Estimation Equation and Calculator
- Viscosity Grade Table ISO 3448
- Airfoil AeroDynamics Characteristics Calculator Mach Number, Reynolds Number, Dynamics Pressure, Viscosity
- Flow Regimes Two flow regimes are laminar flow and turbulent flow
- Laminar Flow Laminar flow (or streamline flow) occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers.
- Turbulent Flow Turbulent Flow Poseuille Law Equation
- Flow Velocity Profiles Not all fluid particles travel at the same velocity within a pipe.
- Average (Bulk) Velocity Ia single average velocity to represent the velocity of all fluid at that point in the pipe.
- Viscosity Viscosity is a fluid property that measures the resistance of the fluid to deforming due to a shear force.
- Ideal Fluid ideal fluid is one that is incompressible and has no viscosity.
- Reynolds Number Reynolds number, based on studies of Osborn Reynolds, is dimensionless number of the physical characteristics of the flow.